Supplemental material 7
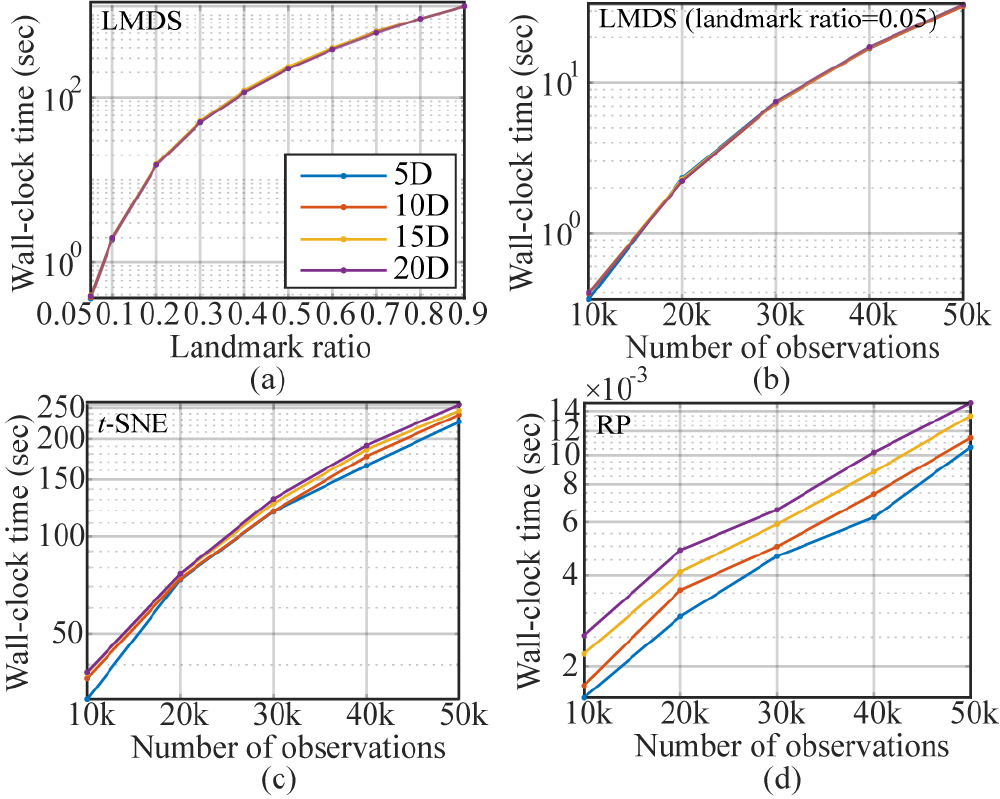
Extended results of speed experiments in logarithmic scale using LMDS, t-SNE, and RP in Figure 11(c). (a) Wall-clock time of LMDS for different numbers of landmark ratios along the x-axis and varying dimensions up to 20D. (b)–(d) Wall-clock time of LMDS, t-SNE, and RP for data sets with different numbers of dimensions (5D, 10D, 15D, and 20D) and observations ranging from 10K to 50K. The wall-clock timings are an average of 10 trials of randomly generated Gaussian data. We note that a ninth-order polynomial can be fitted to LMDS in (a), fourth-order polynomials to both LMDS (b) and t-SNE (c), and a quadratic for RP (d) (norm of residuals < e^-3). Furthermore, the wall-clock time for LMDS heavily depends on the landmark ratio, and LMDS and t-SNE have little difference in wall-clock timings between varying dimensions.